Enabling Remote Extensions on Legacy PBX
Why do we need Remote Extensions on a PBX?
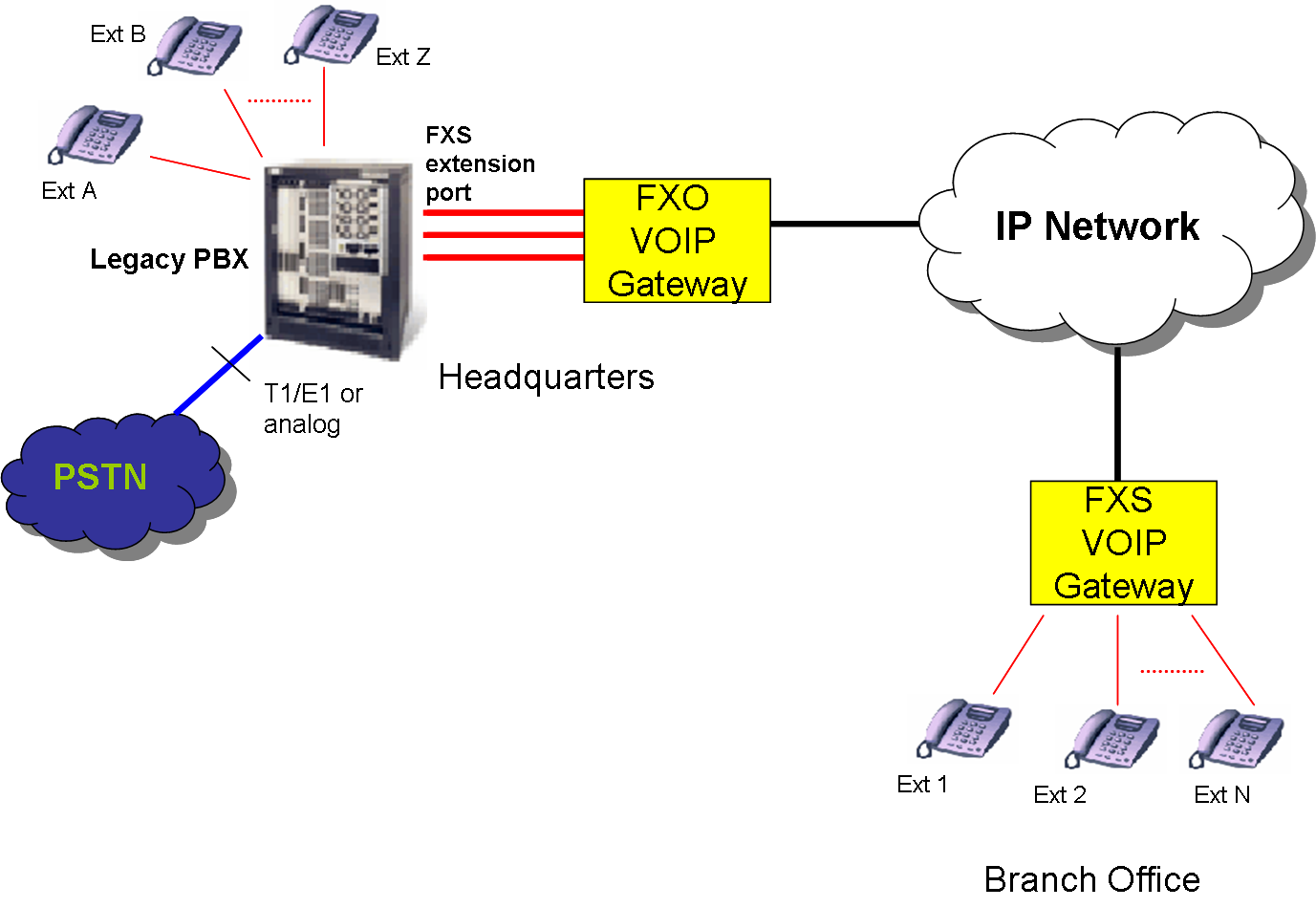
Remote Extension on a PBX enables employees working from home or from a branch office to have an extension of main companies' PBX. The remote employee is given similar facility for communication as their peer is the main office including extension to extension dialing and voicemail. Teleworkers wouldn't need their own landline but use headquarters' trunks and main company numbers for inbound and outbound calls. Savings from eliminated long distance calls between offices and not having to have other PBX or trunk lines in the remote site is another important reason to implement remote extensions.
How does it work?
This applies to legacy PBXs. It won't be required anything other than configuring extension numbers on the PBX; the rest is all transparent for it. The analog extension port of the legacy PBX is virtually extended with the use of an FXO VoIP gateway connected to it and an FXS VoIP gateway in the remote site. When the phone in the branch office dials anything, it would be like the phone is connected to the PBX and dialing. When the PBX rings the extension port in the PBX, the remote phone will ring.
The pair of gateways FXO-FXS converts the analog signaling and transports it over the IP network. Once the call is established the audio will be delivered the same way.
Implementation:
In order to implement this solution it has to be defined the number of remote extensions and based on that use gateways with the same number of ports. We also have to have the same number of extension ports available in the existing PBX. Additional channels might be needed if conference or consultative transfers are performed at the remote site. We assume that there is a reliable IP connection (over the internet or private) between offices with enough bandwidth to support the number of channels needed. Please contact ABP tech to get the hardware and technical help needed.